Ruleset Processing
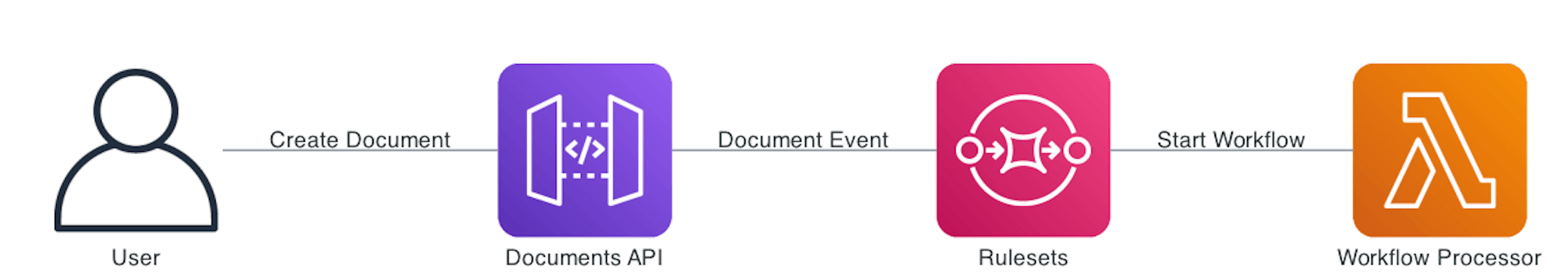
This guide demonstrates how to use Rulesets and Rules to automatically put documents with different content-types into different Queues.
We will be:
-
Creating two document queues
-
Creating two workflows that place the document in one of the queues.
-
Creating a ruleset rule that will place documents in each queue based on the document's content-type
The code for the tutorial can be found on the FormKiQ Github Tutorials
What you’ll need
-
A text editor or IDE - for example IntelliJ IDEA
-
Access to a FormKiQ Advanced/Enterprise installation
-
The
HttpApiUrlfound on the CloudFormation Outputs tab
FormKiQ Client Library
FormKiQ has a client library available in java and python which makes communicating with the FormKiQ application easier.
This tutorial will be using the Java API and required the client 1.14.0 or greater, but will reference the REST API endpoints used.
Setup API
The Java API requires the creation of a ApiClient which requires a JWT AccessToken and the FormKiQ url of the FormKiQ instances to use.
-
A JWT Authentication Token can be aquired using this how-to.
-
The HTTP_API_URL can be found from the "Outputs" tab of the CloudFormation console
private static final String ACCESS_TOKEN = "<ACCESS_TOKEN>";
private static final String HTTP_API_URL = "<CloudFormation Outputs HttpApiUrl>";
The API is broken into sections. In this case, we will need to use the DocumentWorkflowsApi, RulesetApi, and DocumentsApi. These APIs can be instantiated as follows:
/**
* Setup API classes.
*/
public void setUpApi() {
ApiClient client = (new ApiClient()).setReadTimeout(0).setBasePath(HTTP_API_URL);
client.addDefaultHeader("Authorization", ACCESS_TOKEN);
workflowsApi = new DocumentWorkflowsApi(client);
rulesetsApi = new RulesetsApi(client);
documentsApi = new DocumentsApi(client);
}
Create Queues
Using the DocumentWorkflowsApi, create 2 queues
String queueAId = workflowsApi.addQueue(new AddQueueRequest().name(QUEUE_A), siteId).getQueueId();
String queueBId = workflowsApi.addQueue(new AddQueueRequest().name(QUEUE_B), siteId).getQueueId();
The REST API endpoint POST /queues can be used to create a document queue
Create Workflows
Using the DocumentWorkflowsApi, create two workflows, one workflow will put documents into QUEUE_A and the other into QUEUE_B.
String workflowAId = app.createQueueWorkflow(siteId, queueAId, QUEUE_A, "finance");
String workflowBId = app.createQueueWorkflow(siteId, queueBId, QUEUE_B, "management");
String createQueueWorkflow(String siteId, String queueId, String queueName, String approvalRole) throws ApiException {
// Create Workflow Step
AddWorkflowStep step0 = new AddWorkflowStep().stepId(UUID.randomUUID().toString())
.queue(new AddWorkflowStepQueue().queueId(queueId).addApprovalGroupsItem(approvalRole));
// Create Add Workflow Request
AddWorkflowRequest req = new AddWorkflowRequest().name("Queue " + queueName).description("Queue " + queueName)
.status(WorkflowStatus.ACTIVE).addStepsItem(step0);
return workflowsApi.addWorkflow(req, siteId).getWorkflowId();
}
The rest api: POST /workflows can be used to create a document workflow
Create Ruleset
Using the RulesetsApi, create a ruleset that will hold both of our rules.
AddRulesetRequest req = new AddRulesetRequest().ruleset(new AddRuleset().description("Ruleset 1").priority(new BigDecimal(1)).version(new BigDecimal(1)).status(RulesetStatus.ACTIVE));
AddRulesetResponse addRuleset = api.addRuleset(req, siteId);
String rulesetId = addRuleset.getRulesetId();
The REST API endpoint POST /rulesets can be used to create the ruleset
Create Rules
Using the RulesetsApi, create 2 rules. One rule will place all documents with a content-type of "text/plain" into one queue and documents with a content-type of "application/json" into a second queue.
createContentTypeRule(siteId, rulesetId, workflowAId, "application/json");
createContentTypeRule(siteId, rulesetId, workflowBId, "text/plain");
void createContentTypeRule(final String siteId, String rulesetId, final String workflowId,
final String contentType) throws ApiException {
AddRule addRule = new AddRule().description("Workflow " + workflowId).workflowId(workflowId)
.status(RulesetStatus.ACTIVE)
.conditions(new RuleCondition()
.addMustItem(new RuleConditionMust().attribute(RuleConditionAttribute.CONTENT_TYPE)
.value(contentType).operation(RuleConditionOperation.EQ)));
AddRuleRequest req = new AddRuleRequest().rule(addRule);
rulesetsApi.addRule(rulesetId, req, siteId);
}
The REST API endpoint POST /rulesets/{rulesetId}/rule can be used to add rules to a ruleset.
Add Documents
Finally, we will add two documents, one with the content-type of "text/plain" and the other with "application/json".
AddDocumentRequest req0 = new AddDocumentRequest().content("test data").contentType("text/plain");
documentsApi.addDocument(req0, siteId, null).getDocumentId();
AddDocumentRequest req1 = new AddDocumentRequest().content("{\"content\":\"test data\"}").contentType("application/json");
documentsApi.addDocument(req1, siteId, null).getDocumentId();
Check Queues
After the documents are added, it will take between 5-10 seconds for the documents to be placed into the correct queue. You can use the following code to check the queues for each document.
GetWorkflowQueueDocumentsResponse response = workflowsApi.getWorkflowQueueDocuments(queueId, siteId, null, null);
List<WorkflowDocument> documents = response.getDocuments();
The "text/plain" document will be in QueueA and the "application/json" document will be in QueueB.
Summary
And there you have it! We have shown how easy it is to add custom rulesets to allow for the processing of documents based on their content-type.
This is just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to working with the FormKiQ APIs. d
If you have any questions, reach out to us on our https://github.com/formkiq/formkiq-core or https://formkiq.com.